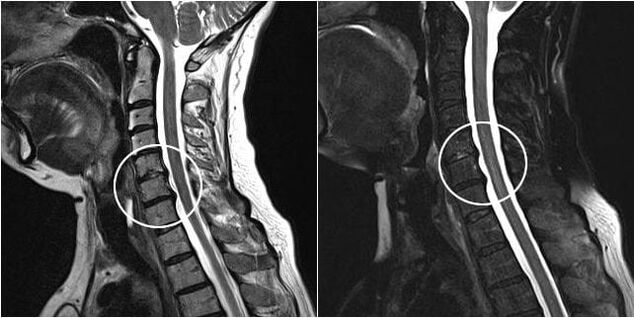
Cervical osteochondrosis is diagnosed more often in women than in men. And this is not only due to the lower strength of the ligamentous tendon apparatus, the weakness of the muscular ligament. Throughout her life, a woman's body is exposed to fluctuations in hormone levels, which can adversely affect the condition of cartilage and bone tissues. But the methods of conservative and surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in both sexes practically do not differ from each other.
Characteristics of female osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in women develops and progresses according to the same scenario as in men. The intervertebral discs lose their ability to retain moisture and slowly collapse, involving the bone structures, ligaments, and tendons in the destructive process. But due to weak neck muscles and more fragile vertebral segments, the first symptoms of the disease appear faster in women. Already at the initial stage of development, pronounced discomfort may appear, which limits mobility.
It should be noted that women of any age have a lower resistance to stress. Having learned the impossibility of a complete cure of osteochondrosis, they can bring themselves to a state of depression with experience. Therefore, antidepressants, antipsychotics, sedatives and tranquilizers are often included in therapeutic treatments.
Causes of the disease in women
The main cause of more frequent damage to the intervertebral discs in women is the decrease or increase in hormone levels in the body. After the onset of natural menopause, the production of estrogens, which are involved in the regulation of the biosynthesis of cartilage and bone tissue, gradually decreases. The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause leads to damage to the discs, leading to the development of osteoporosis (increased bone fragility).
Women monitor their weight, so they often refuse foods with a high calcium content - sour cream, cheeses, peas, soybeans, beans. If the diet is followed, not only does the body weight decrease, but also the lack of the most important trace elements and vitamins occurs, which causes the premature destruction of the intervertebral discs.
Symptoms
In the first X-ray stage, the signs of osteochondrosis are weakly expressed. Only the uneven surface of the intervertebral discs can be observed. Therefore, a woman feels only a slight discomfort in the neck, which occurs after physical exertion or a long stay in a position with the head down. But gradually the intensity of the pain increases. It appears not only when turning and tilting the head, but also at rest. In the absence of medical intervention, the pathology continues to develop. As a result of osteophytes, displacement of the vertebral plates of the artery, the following clinical symptoms appear:
- jump in blood pressure;
- headache (cervical migraine), dizziness, pre-fainting condition;
- reduced visual acuity and hearing, double vision of objects in front of the eyes, tinnitus;
- fatigue, apathy, sleep disorders;
- tickling sensation, "coma" in the throat.

In addition, when the head is tilted or turned, a crackling sound is heard, and the mobility of the neck region is limited.
Diagnosis of pathology
The primary diagnosis can be established on the basis of an external examination, the patient's complaints, and the results of functional tests to assess range of motion, reflexes, and sensitivity. To confirm this, an X-ray is taken in 2 views. The study serves not only to detect osteochondrosis, but also to determine its stage, the degree of damage to the discs and vertebrae. Discography allows accurate examination of the affected intervertebral discs, and if damage to the nerve pathways is suspected, patients are presented with electrophysiological diagnostics:
- evoked potentials;
- electroneurography;
- electromyography.
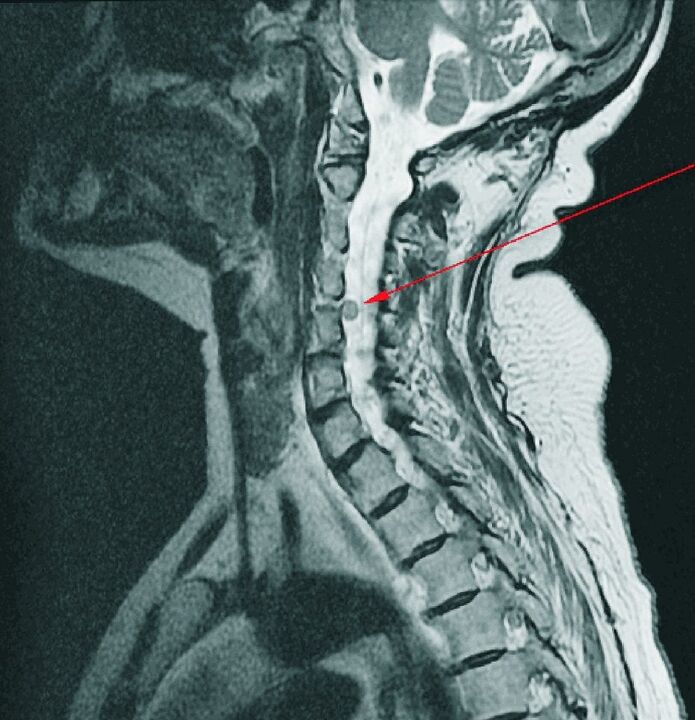
CT, MRI serve as additional diagnostic methods, they are often used to assess the condition of the spinal cord, to detect complications - protrusions or intervertebral hernia. These tests are performed to distinguish between cervical osteochondrosis and spondylitis, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, benign and malignant tumors, ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatism.
First aid in case of exacerbation
During the recurrence of cervical osteochondrosis, there is such a strong pain in the neck that the woman is afraid to turn or tilt her head. To reduce the intensity, lie down on a hard surface. It is necessary to assume a body position in which the pain subsides. If a Shants collar or semi-rigid bandage has already been purchased on medical advice, it must be worn when moving.
Stopping the pain allows you to take any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) pill. Ointments and gels containing NSAIDs have a pronounced pain-relieving effect.
It is not advisable to use cold or heat during first aid. Often a relapse occurs due to muscle spasm, and cold compresses only increase the tension in the skeletal muscles. Dry heating is an effective way to eliminate symptoms, but only if there is no inflammatory process in the soft tissues of the neck.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis in women
Osteochondrosis of any localization has not yet completely healed. A neurologist or vertebrologist must explain to a woman the meaning and principles of the upcoming therapy. The goal of treatment is to achieve stable remission. At this stage, painful sensations occur extremely rarely, and the range of motion is completely preserved.

It is impossible to limit yourself only to taking medicines, since the means for restoring discs and vertebrae have not yet been synthesized. Follow all the doctor's prescriptions - take part in physiotherapy, massage, exercise and gymnastics.
From the first days of treatment, patients are recommended to wear Shants collars - orthopedic devices that stabilize the discs and vertebrae. They prevent the vertebral structures from moving, thereby reducing the likelihood of falls.
Overview of drugs for treatment
Sometimes, when cervical osteochondrosis worsens, burning, stabbing pains occur due to damage to the roots of the spine. They can only be removed by intramuscular administration of NSAID solutions. And if they are ineffective, drug blockades with anesthetics and hormonal agents are used. Glucocorticosteroids are not often used because of their negative effects on internal organs, cartilage and bone tissue.
For mild pain relief, women can take NSAIDs in pill or capsule form. For mild pain, as well as to reduce the dose of systemic drugs, non-steroidal agents in the form of gels and ointments are prescribed.
| A group of drugs for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis | Therapeutic action |
|---|---|
| Chondroprotectors | Partial restoration of the cartilaginous tissues of the intervertebral discs |
| Tools to improve blood circulation | Eliminates oxygen and nutrient deficiency, stimulates regeneration |
| B vitamins | It normalizes the transmission of impulses to the central and peripheral nervous system |
| Muscle relaxants | Relax skeletal muscles, eliminate muscle spasms |
| Warming ointments | It speeds up blood circulation, has an analgesic and anti-exudative effect |
| Antidepressants, sedatives, tranquilizers | It alleviates increased anxiety, restlessness, and sleep disorders |
Physiotherapy, gymnastics, exercises
The most effective way to treat osteochondrosis is daily exercise therapy. With the help of the loads applied to the cervical spine, the muscular ligament is strengthened, the supply of nutrients to the tissues is improved, and the risk of exacerbations is reduced. After stopping the acute pain, you should start gymnastics immediately. A physiotherapist individually compiles exercises for a woman, taking into account her physical fitness and the severity of the pathology. All movements are performed smoothly with a small amplitude. This strengthens the muscles without damaging the cartilage tissue. What exercises do physiotherapists recommend:
- sit up straight, put your hands under your chin. Try to tilt your head, resisting with a brush;
- put your hands on your face while sitting. Tilt your head to the side, resist with a brush;
- stand up, put your hands on your belt. First turn your head in one direction, then the other, without throwing it too far back.
In case of osteochondrosis, swimming, yoga, Pilates, water aerobics, Nordic walking are recommended for patients. Cycling, running and lifting weights are prohibited.

Nutrition and diet
In the case of cervical osteochondrosis, nutritionists recommend limiting the use of alcohol, coffee and strong tea. These drinks interfere with the absorption of calcium and quickly flush it out of the body. Preference should be given to lightly salted mineral waters, fruit compotes and jellies, vegetable juices, and berry fruit drinks. The optimal amount of fluid is 2-2. 5 liters per day.
Fast food, semi-finished products, smoked meats and fatty meats should be avoided. The daily diet should consist of fresh fruits and vegetables, cereals, dried white or rye bread and fermented milk products. Useful turkey, chicken breast, rabbit meat, lamb. Eat some oily fish such as salmon or Norwegian herring 2-3 times a week.
It is better to completely avoid fried foods. The most useful products are baked in foil, steamed or stewed in water.
Physiotherapy
During the rehabilitation phase, patients receive 5-10 physiotherapy sessions. Electrophoresis or ultraphonophoresis is performed with chondroprotectors, solutions of calcium salts, vitamins of group B to restore cartilage tissue, improve innervation and increase the strength of the ligament-tendon apparatus. The same procedures, but only with glucocorticosteroids, painkillers, anesthetics in the subacute period, are used to relieve pain and inflammation.
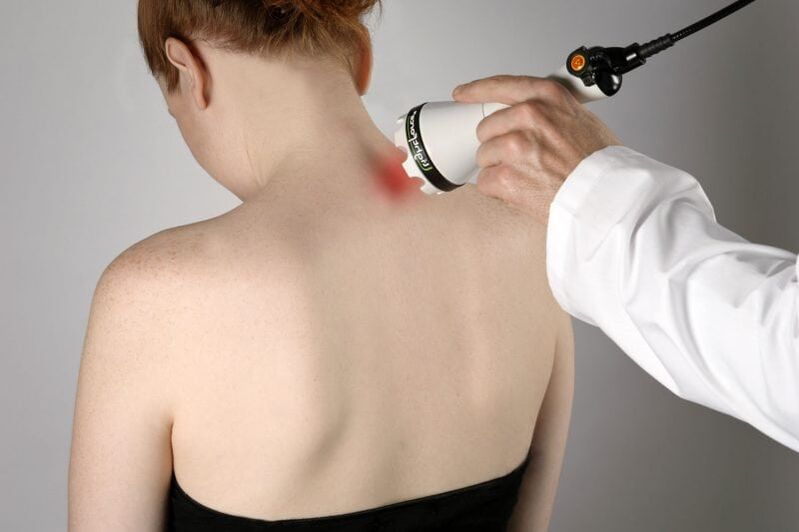
The following physiotherapy procedures can also improve a woman's well-being:

- UHF therapy;
- magnetotherapy;
- galvanic currents;
- laser therapy;
- shock wave therapy.
Applications with ozokerite, bischofite, paraffin are used. The use of medicinal mud and mineral waters, and the use of medical leeches are well proven in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis.
Massages
During the massage, a mechanical effect is exerted on the muscles of the entire back, not only on the neck region. But the specialist pays special attention to them. As a result of performing kneading, smoothing, pressing and chopping movements, spasmodic skeletal muscles relax, ligaments become stronger, and blood circulation improves. The following types of manual and hardware massages are used in the treatment of osteochondrosis:
- classic;
- point;
- vacuum;
- Swedish;
- segmental.
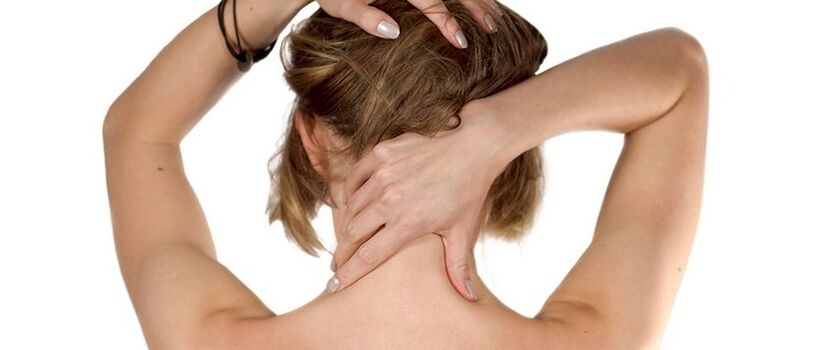
Pharmacies and medical supply stores sell handheld electric massagers. They are equipped with special nozzles and speed controllers. And the comfortable long handle of the devices enables independent massaging of the back of the neck.
Folk remedies
In folk medicine, home-made ointments, alcohol and oil rubs, poultices, decoctions, and tinctures are used to treat osteochondrosis. Representatives of official medicine are skeptical about such therapeutic methods of degenerative-dystrophic pathology, due to their low clinical effectiveness. Exceptions to this are herbal chamomile teas, St. John's wort, and rosehip infusions.

Features of the treatment of older women
The therapy of elderly patients is carried out using the same techniques as the treatment of young women. However, when determining the dosage regimen, the neurologist takes into account the presence of chronic pathologies in the elderly, a decrease in the functional activity of the liver, kidneys and gastrointestinal tract. The doctor chooses drugs that have a mild effect on the internal organs and reduce the risk of side effects.
What is dangerous cervical osteochondrosis
The leading signs of cervical osteochondrosis are similar in both sexes. But the neurological symptoms are more pronounced in women. It is more often diagnosed with damage to the spinal cord roots and the vertebral artery that supplies the brain with nutrients.
In cases of cervical osteochondrosis of the 2nd and 3rd severity, the roots of the spine are often damaged, which leads to the appearance of acute pain, loss of reflexes and a decrease in sensitivity. Serious complications of the pathology are intervertebral hernia, radicular syndrome, discogenic myelopathy.
Preventive measures
Cervical osteochondrosis is often observed in women who prefer narrow, high-heeled shoes. When wearing it, the load on the spinal column is unevenly distributed, which leads to microtrauma of the cartilaginous tissues. Women often suffer from hypothermia, they acutely experience the usual household conflicts. And these factors are prerequisites for the development of pathology. Therefore, their exclusion from the usual lifestyle serves as an excellent prevention of any localized osteochondrosis and its consequences.


























